Enterprise Service Management
One of the latest developments is the transition from a purely IT-centric approach to Enterprise Service Management (ESM). ESM extends the basic principles of ITSM to support not only IT services, but also other operational areas such as HR, marketing, finance and facilities management.
One aspect that is driving the integration of ESM into ITSM practice is the ongoing digitalization and use of new technologies. With the introduction of automation, artificial intelligence (AI) and self-service portals, companies can provide quick solutions to internal issues and offer proactive support. These technologies mean that employees experience more efficient workflows and overall customer satisfaction increases. ESM helps companies understand their services as a holistic system, enabling better coordination and support across all areas.
AI has reached ITSM too
By integrating artificial intelligence, you can automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, freeing up IT teams to focus more on strategic projects. AI-supported tools are able to analyze user requests, recognize patterns and automatically offer solutions, which significantly shortens response times and increases efficiency.
Another innovative aspect of AI in ITSM is the improvement of the user experience through personalized services. Virtual assistants help to process frequent requests quickly and efficiently, resulting in higher end-user satisfaction.
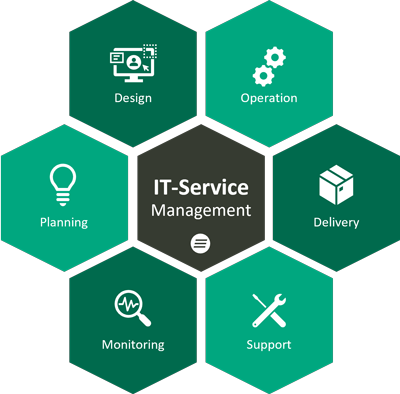
IT Service Management (ITSM for short) is the provision of IT as a service – for employees and customers. This includes all processes and activities related to the planning, compilation, delivery and support of IT services.
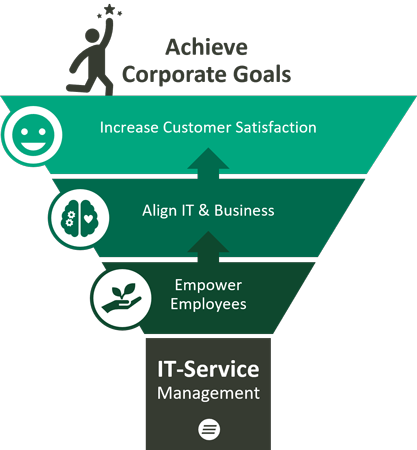
The aim of ITSM systems is to link people, business processes and IT within the company in the best possible way, save time and costs and thus increase productivity and profitability within the company.
In short, ITSM should help to achieve corporate goals and expectations and simplify processes. In addition, ITSM systems help to manage the increasingly complex IT landscapes, IT services and processes more easily and to automate them where possible.
Today, ITSM goes even one step further. Instead of waiting for new application areas and fields of use, many ITSM tools are already taking advantage of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) to predict such requirements as accurately as possible before they arrive.
IT teams are responsible for all IT operations – from newly needed or damaged laptops and faulty servers to business-critical software applications and forgotten passwords, as well as managing and monitoring all relevant enterprise assets, which may well include none-IT assets.
And ITSM offers the best solution for this. This is because it specifies exactly how IT teams must manage and organize the provision of those services for customers and employees so that everyone in the company can work without disruption.
On the other hand, employees and customers can communicate easily with the IT team thanks to ITSM, enabling them to communicate problems and requests with pinpoint accuracy. In contrast to traditional IT support, which merely provides technical tools, ITSM solutions strive to provide a comprehensive and, above all, simple service that effectively supports the internal customer. This enables the IT team to make a measurable value contribution to the company’s success.
Why is IT Service Management important?
Digitalization, hybrid work models and the increasing networking of departments in modern companies today demand efficient IT Service Management. Efficient management of IT services – ideally in real time – is expected by both employees and customers.
In other words, as soon as you offer any IT service or product and are aiming for positive process efficiency, you should be looking at ITSM. ITSM is the only way for IT to respond precisely to the requirements of a company and its customers and employees.
ITSM frameworks, norms and standards
What is an ITSM framework? To ensure that you don’t lose your overview in the dynamic IT environment between constantly changing requirements, technologies and participants, there are so-called frameworks that provide a structure in ITSM. There are also certifications and standards such as ISO/IEC 20000, which contain the minimum requirements for IT service management.
IT teams use a variety of frameworks to guide their work. Among the most commonly used are ITSM and DevOps. However, there are numerous other concepts such as COBIT, SIAM, IT4IT, ITIL and Lean, to name but a few. We list the two most important ones here.
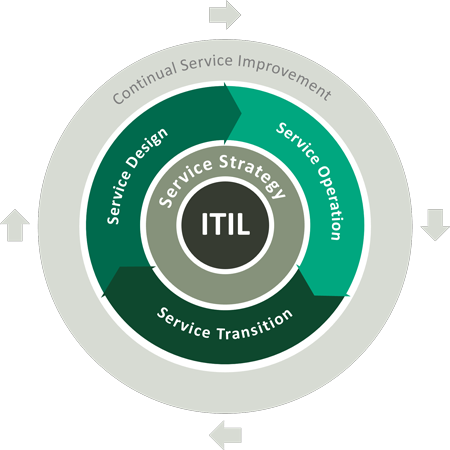
ITIL
The terms ITSM and the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL for short) are often used interchangeably, although they are not the same thing. ITIL is a framework that can be found within ITSM. ITIL’s main focus is on improving efficiency and predictability and is basically a guideline that supports companies in the introduction of ITSM, among other things.
In short, ITIL is a generally recognized set of best practices designed to help an organization get the most out of IT by aligning IT services with business strategy. Methods such as checklists, tasks and processes that any company can easily implement are used for this purpose.
To summarize, it can be said that ITIL processes can be part of ITSM, but not every ITSM uses or follows all the standards defined in ITIL.
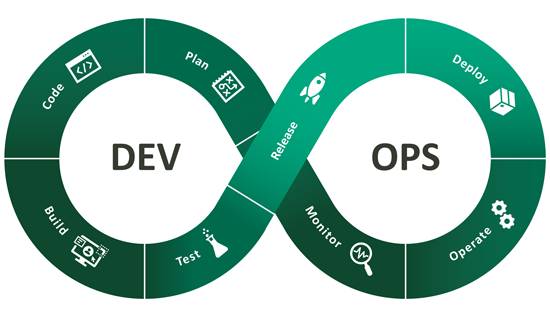
DevOps
DevOps and ITIL are often mentioned in competition with each other, but this is not entirely true: DevOps is a method for bridging the gap between development and operations.
The core principles are open communication, collaboration and shared goals. DevOps and ITIL are therefore not mutually exclusive, but can complement each other. The main difference is that DevOps does not offer process guidelines, as ITIL does. There are countless use cases for DevOps and ITIL, such as:
- the acceleration of new releases
- the prevention of incidents
- the analysis of incidents
- Recommendations for the system structure of ticketing, change and problem management
- Predictive Maintenance
- Ensuring that systems are up to date
- and much more
Now you know what ITSM is, what it does, and what frameworks can go along with it. But what are the specific benefits of implementing IT service management for your company?
The most important task of ITSM software is to improve the efficiency and productivity of a company. This is because the ITSM system reduces costs and mitigates risks, while at the same time making all processes in the company more predictable and easier to plan. And this improved service ultimately leads to a better customer experience, which in turn has a positive impact on business figures.
To ensure this, IT service management acts as a link between end users of IT services and IT specialists. The focus is therefore less on the systems themselves and more on the practical, company-side requirements. Fundamental benefits that result from the implementation of ITSM are the following:
ITSM focuses primarily on planning and managing the IT services of a customer or the employees within a company. This happens through continuous analysis and improvement of existing processes, IT services and infrastructure.
This includes all processes and activities related to the planning, compilation, delivery and support of IT services. ITSM is therefore service-oriented. The central concept stems from the conviction that IT should be provided as a service in order to be able to operate economically.
In addition to these general benefits, ITSM has other benefits to offer the company and the IT department itself, which we list below:
Advantages for the company
Setting up ITSM processes and purchasing IT service management software naturally involves a one-off capital expenditure (CAPEX). However, due to the many advantages mentioned here, you will quickly achieve a higher return on investment (ROI) as you save on recurring operating costs (OPEX). Specifically, companies can benefit from ITSM as follows:
Advantages for IT
But an ITSM system not only has positive effects for the company, IT itself also benefits from the introduction.
In order to really make use of these advantages, IT service management offers a variety of processes, which we will now discuss. It should be noted at the outset that not all processes need to be established in the company, but only those that meet the company’s specific requirements.
Hardly any company can do without technology these days: From the laptop to the applications installed on it, the server to the printer. All these devices are essential for day-to-day work and if they don’t work, entire departments often grind to a halt.
Avoiding long downtimes in the process is often the responsibility of IT, to which most requests of this type are transmitted via a so-called service desk and later handled. In addition to the management of service requests, ITSM activities such as incident management, knowledge management, self-service, reporting a. v. m. edited. Now you can find out which processes can generally be triggered by means of ITSM.
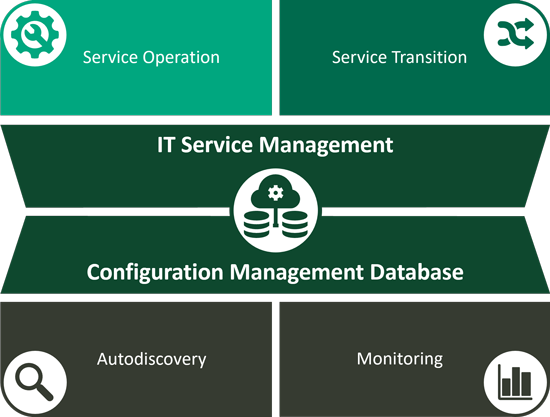
Configuration Management Database (CMDB)
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) stores information about the configuration of items within an organization, including hardware, software, systems, facilities, and sometimes employees. The CMBD therefore forms the central interface in ITSM, as all processes in ITSM access this database.
The aim of a CMDB is therefore to provide the information a company needs to make better business decisions and carry out ITSM processes efficiently. By centralizing all configuration information, managers can better understand critical configuration items and their relationships.
Finding the right ITSM system
We have listed above which advantages ITSM brings to everyday business and which processes it basically covers. In order to be able to meet your individual company requirements and to introduce an ITSM solution that is a perfect fit, the following questions also arise:
- What problem do I want to solve?
- What is missing from your current ITSM processes?
- What can you do to improve your IT services?
- At which points does the ITSM tool come into play?
- What are the requirements for my company?
- Is there collaboration along the central processes even across departmental boundaries?
- Can it be adapted to new requirements as needed?
- Can all relevant corporate assets be managed effectively and do previous processes meet their compliance requirements?
- Would you like to set up a self-service portal?
- What do I expect from a new ITSM tool?
- Are assets monitored as part of a critical infrastructure and to what extent should this be taken over by the ITSM solution (Lifecycle Management, KRITIS)?
In addition, you should also think about the following 2 statements:
- For example, if you want to continue working with different applications, the new tool should have interfaces for connecting them.
- If you have a large number of workflows, you need a tool with workflow automation.
So you see: ITSM systems are modular and can be individually integrated into your company as required. To get the most out of your workflow, you should seek comprehensive advice. Some providers, like us, offer free test runs. The exchange with partners, other companies or customers can also facilitate your decision.
Implementing ITSM in the enterprise: Best Practice in 6 Steps
Note: A successful implementation of ITSM requires the support of IT stakeholders AND business stakeholders. This means that it is of central importance to communicate the relevance of ITSM within the company.
The introduction itself requires precise planning of the most important success factors, as well as the control of the same by means of regularly monitored key figures. One basic way of advising companies on the successful implementation of ITSM is to look at current IT processes (for example, “new employees”), track them, divide them into several steps and digitize them. The basic procedure for this is as follows:
If we look to the future of ITSM, we can see the rise of so-called AIOps. The term AIOps is composed of Artificial Intelligence, AI, and the management of IT operations, Ops. Artificial intelligence is used to report and solve operational difficulties (such as system failures) or to look for ways to keep pace with and manage the increasing complexity of technologies.
One of the most important tasks for AIOps is the integration of the most diverse data silos from ITSM and IT operations management. This pooling of data makes it increasingly easy to discover the causes of many problems more quickly and efficiently and therefore to resolve them. At the same time, it also helps to enable automation in the first place, as there is only a single data pool instead of individual silos. As with many technologies, the future of ITSM also lies in AI, or artificial intelligence. Through the automation of numerous areas, …
- like automated communication,
- ticket solution,
- automatic workload optimization and
- preventive maintenance of systems
… a lot of time can be saved. This is because AI can permanently monitor the Service Desk’s infrastructure and detect and report incidents at an early stage.
ITSM: Benefit from IT Service Management today
ITSM benefits not only your IT team, but your entire organization. When used correctly, ITSM always leads to an increase in efficiency and productivity. That’s because a structured ITSM approach enables IT alignment with business goals and standardizes service delivery based on budgets, resources and outcomes – for employees and customers. This reduces costs and minimizes risks, which ultimately has a positive impact on the entire company and its public image.